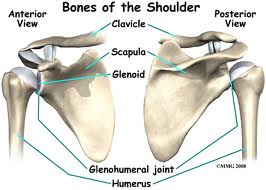
- Articular Capsule
- Glenohumeral Ligament
- Coracohumeral ligament
- Transverse Humeral Ligament
- Glenoid Lambrum
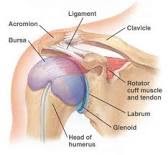
- Bursa
- Sub-acromial bursa
- Sub-coracoid bursa
- Sub-scapular bursa
- Sub-deltoid bursa
- Movements
Anterior fibres of deltoid
Pectoralis major
Biceps
Coracobrachialis
Extension:
Posterior fibres of deltoid
Latissimus dorsi
Teres major
Abduction:
Middle fibres of deltoid
Supraspinatus
Adduction:
Pectoralis major
Latissimus dorsi
Teres major
Teres minor
Lateral rotation:
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Medial rotation:
Subscapularis
Latissimus dorsi
Teres major
Elbow Joint
The synovial hinge joint formed by the articulation of trochlear notch of ulna and head of radius with trochlea and capitulum of the humerus. It is extremely stable joint of the body having the following characteristics.
- Articular Capsule
- Annular Ligament
- Ulnar Collateral Ligament
- Radial Collateral Ligament
- Movements
Brachialis
Biceps brachii
Brachioradialis
Pronator teres
Extension:
Triceps
Anconeus
Proximal Radioulnar Joint
The pivot type of synovial joint formed by the articulation of radial head with radial notch of ulna.
Distal Radioulnar Joint
The pivot type of synovial joint which is formed by the articulation of ulnar head with ulnar notch of radius.
- Movements
Pronator teres
Pronator quadratus
Supination:
Biceps brachii
Supinator
Wrist Joint
The condyloid type of synovial joint formed by the distal end of the radius and the articular disc of the distal radioulnar joint with the proximal row of carpal bones except the pisiform i.e scaphoid, lunate and triquetrium.
- Movements
Radial (abduction) deviation
Ulnar (adduction) deviation
Circumduction
Carpometacarpal and Intermetacarpal Joints
These all are plane synovial joints except that of thumb which is saddle joint.
- Movements
Metacarpophalangeal Joints
These are condyloid type of synovial joints which allow movement in two directions.
- Movements
Extension
Abduction
Adduction
Circumduction
Interphalangeal Joints
These are uniaxial hinge joints which allow movement in only on direction.
- Movements
Extension
Pectoral Girdle
The pectoral girdle(clavicle and scapula) connects the upper limb to the trunk, therefore, its articulations are includeed with those of upper limb.
Sternoclavicular Joint
This is a saddle type of synovial joint and is the only bony articulation between the upper limb and the axial skeleton.The medial end of the clavicle articulates with the manubrium of the sternum.
- Movements
Acromioclavicular Joint
This is a plane type of synovial joint. Acromial end of the clavicle articulates with the acromion of the scapula.
The acromion of the scapula rotates on the acromial end of the clavicle.
 8:07 AM
8:07 AM
 Aftab Ahmad Khan Yousafzai
Aftab Ahmad Khan Yousafzai











 Posted in:
Posted in: 








0 comments:
Post a Comment